Automation through Cypress is easy: Five major commands and one assertion
Overview
Here we will look at the overview of command in the cypress. Cypress command queries the DOM and make things happen. There are different commands to perform different tasks in the DOM which we will cover here.
Before going through the commands, the basics of cypress is necessary so Click Me.
I prefer learning from the folder structure because it makes it easier to know the right place for the code. If you want to learn about the folder structure then Click Me. The folder structue is of older cypress version. But this can also give you overview.
Cypress is built on top of Mocha and Chai. Here the coding format looks similar to Mocha and Chai. Here we will look at the general automation test in cypress. It uses the mocha interfaces like describe(), it(), context() and specify().
Here, describe() is used for the general description about the test that is going to carry out and it() contains the specific test. Let’s see through an example.

The description combines the related test (i.e. it blocks). The description describes the test on the home page and each (it) block has a different test on the home page. This is the general flow. Now let’s see the commands to manipulate the DOM.
Actions:
cy.visit():
This cy.visit command takes two params; one is url to visit the site and other is options. Options are optional.
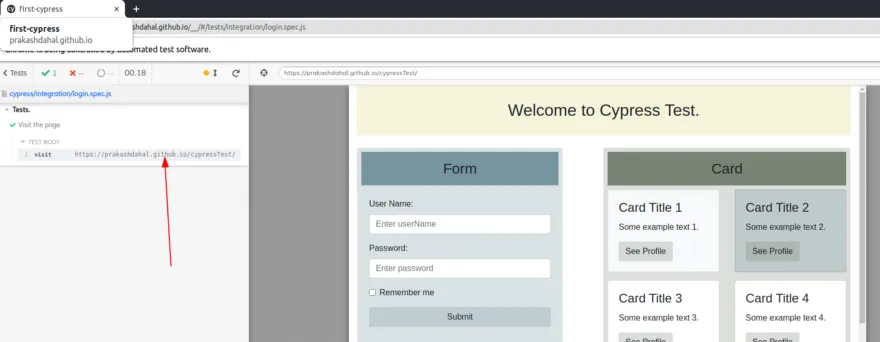
Example:
a. cy.visit(“https://google.com”)
b. cy.visit(“https://google,.com”, {timeout: 30000})
We can pass options in a key value pair like timeout which is optional but the first parameter (i.e. url) is compulsory.
Generally, we do have the same domain where we perform the test. The url of the domain can be stored in the cypress.config.js file as baseUrl (The old version of cypress uses cypress.json).
const { defineConfig } = require("cypress");
module.exports = defineConfig({
e2e: {
baseUrl: "https://YourBaseUrl.com",
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
// implement node event listeners here
},
},
});
Now, the baseUrl can be accessed by all the test files. So, in the test file, cy.visit command can be used. We can pass forward slash (/) i.e. cy.visit("/").
If we want to visit home page then we can pass “/home” in cy.visit.
To learn more, click me
cy.get()
We can get any element of the DOM through this command. This command takes string params. Its like a jQuery selector.
Lets see examples; cy.get(‘h1’) cy.get(‘.className’) cy.get(‘#idName’)
Here we can pass element tags like h1 and it gets the h1 value. Similarly we can pass class and id.
Note: ClassName is followed by period “.” and ID is followed by “#”
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("h2");
});
});
This command has got the h2 element. Similarly, we can get the information from classes and ids.
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("h2");
cy.get(".card-title");
cy.get("#userName");
});
});
To learn more, click me
cy.type()
If we get an input field then we can type value in it.
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("h2");
cy.get(".card-title");
cy.get("#userName").type("First type");
});
});
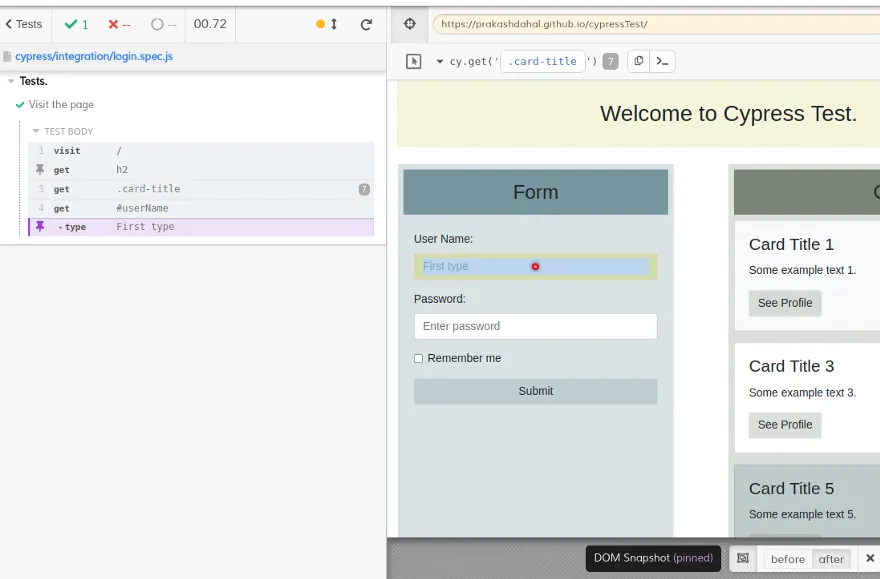
To learn more, click me
cy.contains()
We can get the information through value as well. We can search for contains.
Lets see an example
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("#userName").type("First type");
cy.contains("Submit");
});
});
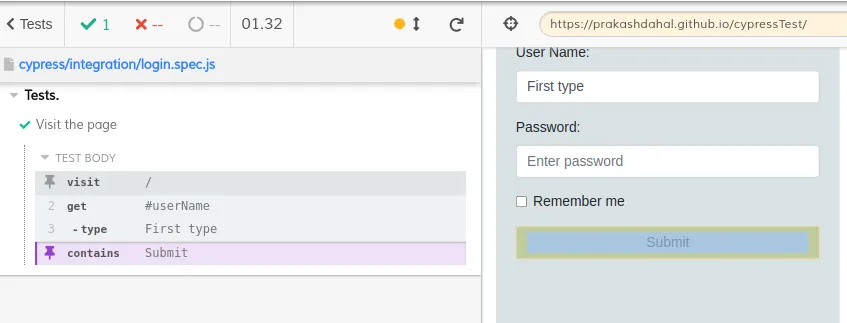
To learn more, click me
cy.click()
We can click into the element like button. The command is cy.click()
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("#userName").type("First type");
cy.contains("Submit").click();
});
});
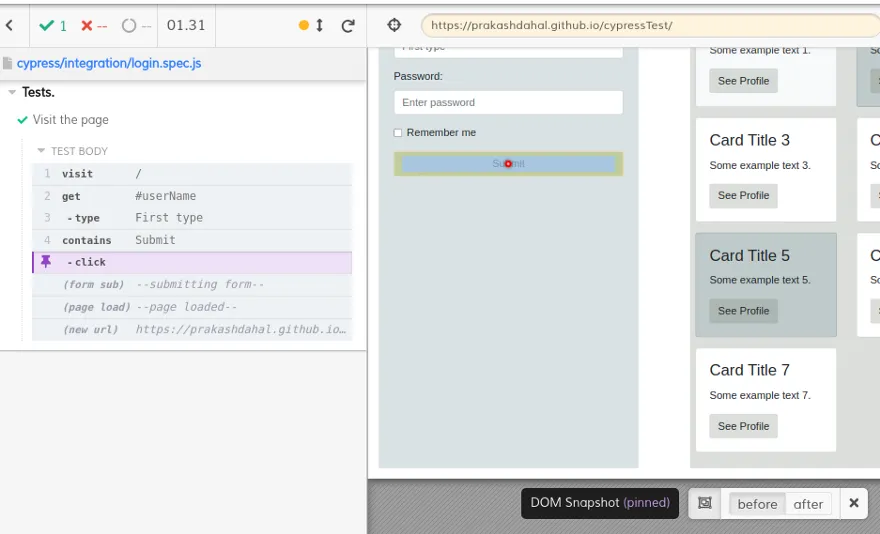
To learn more, click me
These are the major commands to take actions in the DOM. There are other useful commands like clear(), dblClick(), rightClick(), hover() and so on. To learn these commands, click me
Assertions:
While testing, after taking some actions; we ensure that the action carried is giving us the proper result. The assertion commands are given below:
The major commands for assertion is should() and expect(). Here we will discuss more about should().
should(‘contain’, ‘text’)Here the first parameter is keyword ‘contain’ and second one is text. This command is used to check whether that text is included in the element or not.
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("h2").should("contain", "Welcome");
});
});
should(‘have.class’, ‘className’)
We pass have.class keyword as first parameter and the className as second parameter. This will check that the element has that particular class or not. Example; If a button has to be disabled class then we can check this through this command.
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("h3").should("have.class", "bg-blue");
});
});
> Note: if we have to ensure that the particular class should not exist then, should(‘not.have.class’, ‘className’) can be passed. if we want to check css on the particular element then, should(‘have.css’, ‘font-family’).
should(‘be.visible’)
To check the visibility of the element, be.visible parameter can be used.
describe("Tests", function () {
it("Visit the page", () => {
cy.visit("/");
cy.get("h3").should("be.visible");
});
});
> Note: if the particular element should not be visible then, should(‘not.be.visible’) can be passed.
To learn more about should command, click me. We can pass other many keywords like should(‘have.length’), should(‘equal’, ‘text/number’) and so on.
You can learn about expect() command as well.
Conclusion
These are some major commands used in cypress for actions and assertions. Now, if you know these things then you can easily perform automation tests through cypress.
There is still a lot to learn but these basics will help you learn further easily.